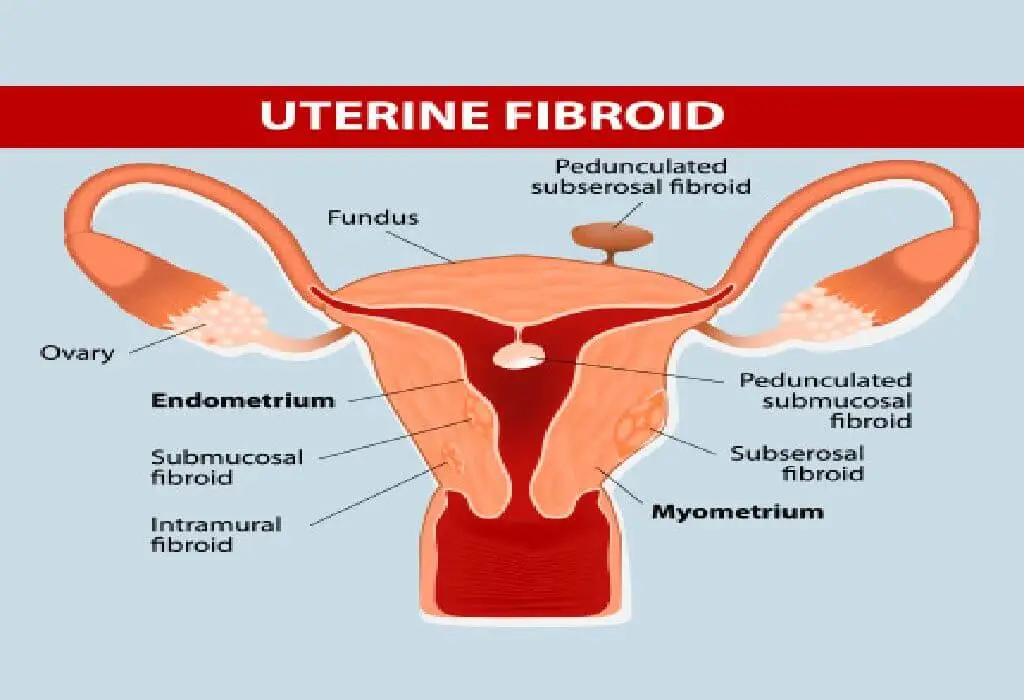
Uterine fibroid in women are not uncommon to find out. Whether these non-cancerous tumours found inside the uterus will affect a woman’s health depends on their exact location.
They are found within the uterus are benign tumours created from an equivalent muscle fibres because the myometrium. The myometrium is that the middle layer of the uterine wall. Consisting mainly of uterine smooth muscle cells (also called uterine myocytes), but also supporting stromal and plant tissue .
Fibroids are dense and round in shape. When these fibroids are located under the liner membrane outside the uterus (serosa), they’re called subserosal fibroids. Submucosal fibroids are formed inside the cavity , under the uterus lining, and intramural fibroids are contrived within the muscular wall of uterus.
Symptoms of Uterine Fibroid
Most women experience mild to no symptoms, but several others can undergo pain and heavy bleeding during their monthly periods. Symptoms may manifest within a couple of months of development. It sometimes take years to point out up. The symptoms and problems related to uterine fibroids include:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding and prolonged periods.
- Spotting before or after a painful menstruation.
- Abdomen, pelvis and lower back aches.
- Pain during sexual activity .
- Frequent urination and enuresis .
- Pain with bowel movements.
- Inability to conceive.
- Problems like placental abruption, premature delivery and miscarriage.
Can Uterine Fibroid Cause Infertility and Miscarriage in Women?
Research has shown that uterine fibroids can reduce fertility by an approximate 70 per cent. They also are linked with increased rate of miscarriage and premature delivery.
In some cases if the fibroids grow large, they will narrow down the cavity. It will led to increasing the danger of miscarriage and infertility. Usually fibroids affect fertility once they grow inside the uterus, hindering embryo implantation or resulting in early miscarriages.
However, some women give birth to healthy babies despite having large fibroids. So, there’s no evidence on how and when uterine fibroids affect fertility.
In case of a miscarriage, the submucosal fibroid affects the fertilized egg within the uterus lining. During the primary and second trimesters, the fibroid can thin out the liner and reduce the blood supply. It can lead to causing underdevelopment of the fetus and eventually miscarriage. But a consequent pregnancy can proceed with none issues. This is due to the likelihood of the egg settling at another location within the lining.
Treatment
Uterine fibroids often don’t require treatment. Only women with fibroids have problems like acute pain. Apart from that, blood loss during monthly period, inability to conceive and miscarriage. The doctor makes appropriate recommendation. a number of the treatments available are:
- Endometrial Ablation
Fibroids that grow within the inner layer of the uterus are often treated with this procedure. The fibroid growing endometrial tissue is faraway from the inner lining with laser energy. Also, a heated wire loop, or hot fluid during a balloon. - Myolysis
With laparoscopy, it’s a minor surgery. Its about inserting a small needle to probe or send current straight into the fibroid to burn it also as surrounding blood vessels.
- Myomectomy
This surgery is best suitable for women who decide to have children in future. The surgeon removes the fibroids leaving the uterus intact during this challenging procedure. Just in case the fibroids grow outside the cavity, the doctor will perform a laparoscopic myomectomy. - Hysterectomy
This procedure is for women who are nearing menopause or aren’t getting to have children. This procedure is all about removing the whole uterus.
- Arteria Uterina Embolisation (UAE)
Advanced X-rays are done by radiologists to work out the precise location of fibroid. Therefore the surrounding blood vessels. Then the blood supply to the fibroid is stop by injecting a plastic plug into the vessel. Without adequate blood, the fibroid shrinks down and dies. - Medication
Some practitioners recommend medication that reduces the estrogen’s levels, eventually shrinking the fibroid and/or temporarily interrupting its growth. However in many cases, these can start growing after the medication stops.
There are not any specific ways to stop fibroids from developing or recurring. You may want to consult top gynecologist if you notice any symptoms. Your doctor will offer you the simplest advice and recommend a treatment, if required.